
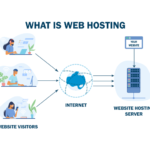
Cybersecurity involves safeguarding internet-connected systems, which include hardware, software, and data, from potential cyberthreats. It is a vital practice employed by both individuals and businesses to prevent unauthorized access to data centers and other computerized systems.
These threats can take various forms and may target individuals, businesses, or even governments. Some common cybersecurity threats include:
- Malware: Malicious software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system or network. Types of malware include viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, and adware.
- Phishing: Deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details, by disguising as a trustworthy entity in electronic communication. Phishing attacks are commonly carried out through email, text messages, or fraudulent websites.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks: These attacks aim to disrupt the normal functioning of a system or network by overwhelming it with a flood of traffic, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks: In this type of attack, a cybercriminal intercepts communication between two parties to eavesdrop, manipulate data, or steal information, often without the knowledge of the communicating parties.
- SQL Injection: An attack where malicious code is inserted into a web application’s database query, allowing the attacker to access, modify, or delete data stored in the database.
- Ransomware: Malware that encrypts files or systems, rendering them inaccessible until a ransom is paid. Ransomware attacks have been increasingly targeting businesses and organizations, causing significant disruptions and financial losses.
- Zero-day exploits: Vulnerabilities in software or hardware that are unknown to the vendor or developer. Cybercriminals exploit these vulnerabilities before a patch or solution is developed and implemented, leaving systems at risk.
- Insider threats: Risks originating from within an organization, where employees or individuals with privileged access misuse their authority to steal data, compromise systems, or cause damage.
- Social Engineering: Psychological manipulation of individuals to trick them into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that may compromise security. This can include tactics like pretexting, baiting, or tailgating.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Complex and sophisticated cyber attacks that often involve a prolonged and targeted effort to breach a network, with the intention of stealing sensitive data or monitoring activities over an extended period of time.
It is important for individuals and organizations to stay informed about these threats and to implement robust cybersecurity measures, including regular software updates, employee training, strong authentication methods, data encryption, and the use of reliable security software and firewalls to protect against these risks.














































































One thought on “Risks of digital systems in the world of Tech”