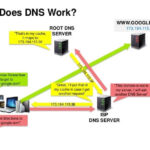
Hacking refers to the act of gaining unauthorized access to computer systems or networks for various purposes, including testing security, identifying vulnerabilities, or committing cybercrimes. Here are some notes on the advantages and disadvantages of hacking:
Advantages of Hacking:
- Identifying Vulnerabilities: Ethical hackers or security professionals can use hacking techniques to identify weaknesses in a system’s security, helping organizations strengthen their defenses against malicious attacks.
- Improving Security Measures: Hacking activities can prompt companies to invest in stronger security measures, leading to more robust protection against potential cyber threats.
- Advancing Technological Understanding: Hacking often requires an in-depth understanding of technology, which can push the boundaries of technological understanding and development.
- Detecting Malware and Threats: Skilled hackers can help in detecting and mitigating malware and various cyber threats, thereby reducing potential risks for organizations and individuals.
Disadvantages of Hacking:
- Security Breaches: Unethical hacking can lead to security breaches, resulting in the compromise of sensitive information, financial losses, and damage to the reputation of the affected entity.
- Privacy Violation: Hacking can lead to the invasion of privacy, with personal and sensitive information being exposed, exploited, or misused without consent.
- Illegal Activities: Unlawful hacking activities can result in legal repercussions, including hefty fines and potential imprisonment, depending on the severity of the offense.
- Cyber Threats and Attacks: Hacking can contribute to the proliferation of cyber threats and attacks, leading to a more vulnerable digital environment and widespread disruption of services.
- Erosion of Trust: Frequent hacking incidents can erode the trust of users in technology and digital systems, leading to a reluctance to embrace technological advancements.
It is essential to differentiate between ethical hacking, which aims to improve cybersecurity, and malicious hacking, which is aimed at exploiting vulnerabilities for personal gain or causing harm. Ethical hacking, also known as penetration testing, is conducted with the consent of the organization or individual and aims to improve cybersecurity measures. On the other hand, malicious hacking is a criminal activity that can lead to severe legal consequences.